What is verb?
A word that expresses either an action or a state of being in a sentence is called verb. It is called the soul of a sentence. So, every sentence must have a verb.
There are three types of verb:
1) Action verbs 2) State of being verbs 3) Linking verbs
What is action verb?
An action verb describes an action in a sentence. An action means something happening.
Example:
I‘m cleaning the room.
The student is buying a pencil.
He put the book on the shelf.
Action verb can be simple or continuous.
Some action verbs: run, jump, kick, eat, break, cry, smile, think, etc.
What is state verb?
A state verb describes a state in a sentence. A state means something staying the same.
The room is clean.
The student owns this pencil.
The shelf contained these books.
State verbs cannot usually be continuous.
Incorrect: The student is owning this pencil.
Some state verbs: be, believe, belong, exist, hate, know, like, love, matter, consist of, contain, depend on, deserve, mean, own, need, prefer, remember, resemble, seem, understand.
What is linking verb?
The verbs that link the subject of a sentence with a noun or adjective (complement) are called linking verb. Linking verbs do not describe action.
Example:
Nipa became a famous writer.
The problem seems easy.
The tin grew hot.
Jaman appeared uninjured after the accident.
The bird looks nice.
There are 13 linking verbs:
To be verb = be, am, is, are, was, were, been, being.
State of being verb = appear, seem, become, grow, turn, prove, remain
Five senses = look, sound, smell, feel, taste.
Difference between linking verb and state verb
Linking verbs and state verbs have many similarities as words. But they are very much different in function.
Linking verbs join the subject with noun or adjective as complements.
She looks nice. (Here, the word ‘look’ connects the subject ‘she’ with the adjective ‘nice’.)
Mr. John is a doctor
Ice feels cold.
State verb refers to a state of the subject.
Rose smells sweet.
Here, smells refers to a state of the flower rose. So, the word ‘smell’ is a state verb.
How to identify a verb in a sentence?
- Generally, a verb shows an action or describes something
If we ask a question to a subject –
What does? Or what does S (subject) do? Or What is the action of subject?
Example: Shelly eats an apple. Question: What does Shelly do? Answer: Eat (verb)
We shall certainly get a verb in answer. Thus we can identify a verb.
- Verb is the time of an action. If we change the time of a sentence, we shall be able to detect the change also in verb.
Example:
Mr.John goes to office today.
Mr.John went to office yesterday.
Mr.John will go to office Tomorrow.
Thus we can find a verb in a sentence.
- To find a verb, we place the word after pronoun. If it is verb, we shall find that it makes sense.
I _____. You _____. He _____. She _____.
It _____. We _____. They _____.
Example: I write. ( It makes sense So, the word ‘write’ is a verb.)
I mango ( It doesn’t make sense. So, the word ‘mango’ is not a verb.)
Different types of verb
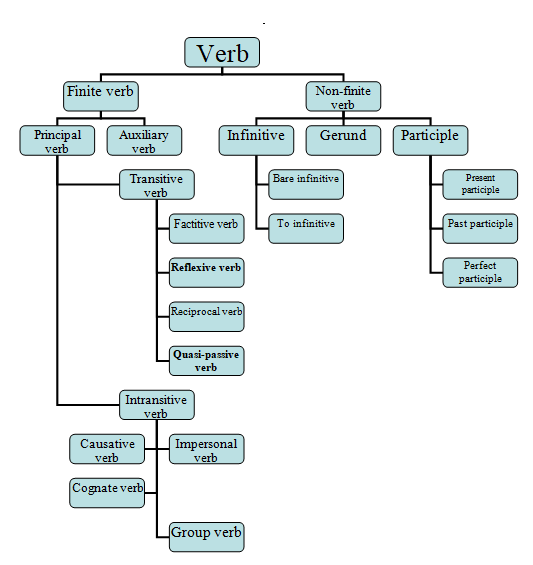
Mainly there are two types of verb.
1) Finite verb 2) Nonfinite verb
Finite verb: A finite verb is a verb that shows agreement with subject and is controlled by tense. A finite verb is completely inflected. It is modified to express different grammatical categories such as tenses, person, number, gender, moods, or voices. Generally, a finite verb completes the meaning of a sentence.
Example:
I go to the shop.
She goes to the shop.
They went to the shop.
Types of finite verb
Among finite verbs, there are two sub-types:
1) Principal or Main verb.
2) Helping or Auxiliary verb
Principal or Main verb: Main verb means an important verb of a sentence. It tells us about the action or state of being of the subject. It can stand alone or can be used with helping verb.
The boy plays football.
Helping or Auxiliary verb: The term refers to the verb that helps the main verb to complete the sentence.
It appears in a sentence to express different tenses, moods, or voices. The combination of helping verbs with main verbs creates verb phrases.
He is eating rice.
They have done the work.
I do not eat rice.
This work is done to help the poor.
There are three types of helping / auxiliary verb:
- Primary helping verb (3) –> Be, Have, Do
- Modal helping verb (10)—> Can, Could, May, Might, Shall, Should, Will, Would , Must, Ought to
- Semi-modal verb. (3)—> Need, Dare, Used to
Nonfinite verb:
A non finite verb is a verb that cannot perform the action or do not work as a verb completely in a sentence.
They typically are not inflected by grammatical tense, person, number, gender etc. and have little inflection for other grammatical categories. Nonfinite verbs may be coupled with a finite verb in a finite clause.
Reading books is my hobby. (Reading – Gerund (non-finite); is – finite)
He likes reading. (Reading – Participle (non-finite)
He likes to read. (To read – Infinitive (non-finite)
Types of non-finite verbs:
- Infinitive, 2) Gerund, 3) Participle.
Infinitive: Infinitive verb is the basic dictionary form of a verb. Infinitive verbs are not usually inflected for tense, person, etc.
There are two forms of infinitives.
- Bare infinitive,
- full infinitive or to-infinitive
The form of verb which is without to is called the bare infinitive.
Example: I can sit here all day.
The form of verb which is with to is called the full infinitive or to-infinitive.
Example: I want to sit on the other chair.
Participle: A participle is a form of a verb that plays a role in a sentence similar to an adjective or adverb.

Example:
The sleeping cat is brown.
The freshly picked tomatoes look delicious
Types of participle

Gerund : Gerunds are words that are formed with verbs but functions as a noun.
Example: – Swimming is fun.

Types of principal verb
1) Transitive verb
2) Intransitive verb
Transitive verb: A verb that takes a direct object to complete the sense of the sentence is called transitive verb.
INCOMPLETE : COMPLETE :
The shelf holds______? Hold what? The shelf holds three books and a container of flowers.
She gave _____? Gave what? She gave money to the cashier.
Intransitive verb: A verb, that does not take an object, is called an intransitive verb.
We walk to the railway station. ; Walk what? No answer. (No object)
The birds are flying. ; Flying what? No answer. (No object)
Types of transitive verb
1) Factitive verb
2) Reflexive verb
3) Reciprocal verb
4) Quasi-passive verb
Factitive verb: Factitive verbs are the verbs that require an objective complement as well as an object to complete its action. It indicates the resulting condition or state of a person, place, or thing caused by the action of the verb.
Example: We made him captain.
The company appointed him chairman.
[Factitive verbs include Name, think, make, select, elect, nominate, appoint choose, deem, assign, judge, and designate etc.]
Reflexive verb: A reflexive verb is a verb whose direct object is the same as its subject. That means the subject and object always refer to the same person or thing, and the object is always a reflexive pronoun.
I am teaching myself to speak English.
Types of Intransitive verb:
1) Causative verb
2) Impersonal verb
3) Cognate verb
4) Group verb
Causative verb: A causative verb is a verb that causes someone or something else to do or causes a change in state.
Examples of causative verbs: make, cause, allow, help, have, force, enable, keep, hold, let, and require.
She made her children do their homework. ;
[make /Let+ person /thing + base form of verb]
Too much water makes plants turn brown.
John let me drive his new car.
He got the letter written. [get + thing + participle]
Let’s get Monir to go with us. [get + person + to + verb]
My English teacher had us give oral report. [have + person + base form of verb]
I want to have this book renewed , please. [have + thing + participle]
Cognate verb: A cognate verb is a verb that is ordinarily intransitive and takes the cognate object a noun to complete the sentence. Cognate object is a noun whose meaning closely resembles to Cognate verb.
Example:
He ran a race.
Tania sang a song.
I slept a sound sleep.
Related term:
