
Tense is the time of an action or state of a verb.
The word tense has come from Latin word ‘tempus’ that refers to “time”. Time refers to the moment when an action takes place. There are three times in the timeline. They are past, present and future.
Verb is the word in a sentence that conveys an action or state. So, verb of a sentence relates to time. Verb changes its form to show different times like past or present or future.
So, tense is a form of verb that indicates the time of action or state.
There are three grammatical tenses. They are present, past and future tense.
Present tense: The form of verb that refers to the present time is said to be in the present tense.
The boy gives me a book to study.
Past tense: The form of verb that refers to the past time is said to be in the past tense.
The boy gave me a book to study.
Future tense: The form of verb that refers to the future time is said to be in the future tense.
The boy will give me a book to study.
Aspect
Again, aspect is a term that expresses how an action or state extends over time in a sentence. In other words, the category of aspect says how a state or action relates to time.
During the process of an action within a particular tense four states of action may take place in different duration of time. They are whether the actions are in complete or in progress or already completed but expecting an outcome, or in a repeated situation.
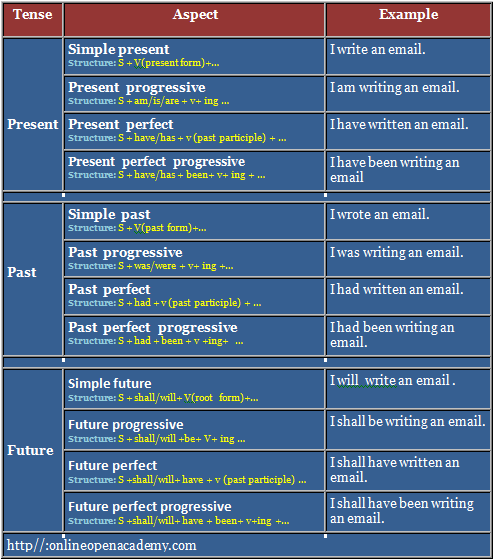
So, in English grammar, there are three tense and four aspects.
The four categories of aspect for each tense in English are as follows:
- Simple
- Continuous/Progressive
- Perfect
- Perfect continuous/ perfect progressive
The category of aspect is linked with the category of tense.
Here are all verbal aspects in English.
1) Simple Aspect
The simple aspect is the aspect of verb form used to express a fact, a complete action or a habitual action.
Mikhail Shchennikov walks fast in the world. (A fact)
John walked three kilometers in the morning yesterday. (Completed action)
My father walks two kilometers every morning. (Habitual action)
Simple aspect covers three categories. They are the simple past tense, the simple present tense, and the simple future tense.
Verb form of each category is as follows.
Simple present tense: Generally the verb form is present form of verb. According to subject-verb agreement, if subject of a sentence is third person and singular number, the verb form receives s or es.
I eat breakfast.
He eats breakfast.
Simple past tense : The verb form is past form of verb.
He ate breakfast.
Simple future tense: The verb form is ‘shall/will + base form of verb’.
He will eat breakfast.
2. Continuous/Progressive aspect
The continuous and progressive aspect is the verb form to express the incomplete state of an action or the action in progress at specific time.
Continuous and progressive aspect includes different form of verb in past ,present and future time. They are as follows.
Present progressive aspect: The verb form is ‘am/is/are + (verb+ing)’.
He is eating breakfast.
Past progressive aspect: The verb form is ‘was/were + (verb+ing)’.
He was eating breakfast.
Future progressive aspect: The verb form is ‘shall be/will be + (verb+ing)’.
He will be eating breakfast.
3. Perfect Aspect
The perfect aspect is the verb form to express an action or circumstance occurred earlier than the time under consideration focusing on the resulting state rather than on the occurrence itself.
Perfect aspect includes different form of verb in past, present and future time. It should not be confused with tense.
Present perfect aspect: The verb form is ‘have/has + past participle form of verb’.
He has eaten breakfast.
Past perfect aspect: The verb form is ‘had + past participle form of verb’.
He had eaten breakfast.
Future perfect aspect: The verb form is ‘shall have/will have + past participle form of verb’.
He will have eaten breakfast.
4) Perfect progressive aspect
The perfect progressive aspect is the form of verb to express an action that was once ongoing, but has since completed. Two actions work together here for long.
In this aspect, the form of verb changes with tenses.
Present perfect progressive aspect: The verb form is ‘have/has + been + (verb+ing).
He has been eating breakfast.
Past perfect progressive aspect: The verb form is ‘had + been + (verb + ing)’.
He had been eating breakfast.
Future perfect progressive aspect: The verb form is ‘shall have/will have + been + (verb + ing)’.
He will have been eating breakfast.
Tense – aspect chart in combined :
Related pages :
