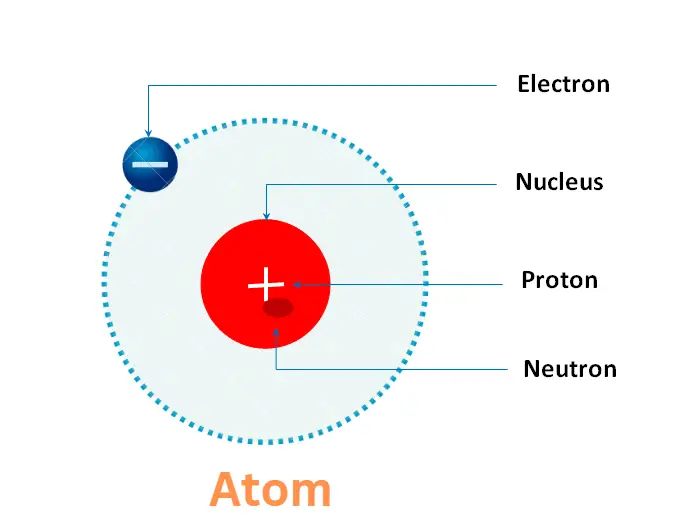
Structure of Atom
Atom is the basic unit of a substance. It consists of a nucleus, which contains positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons, surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
The nucleus is located at the center of the atom and contains most of its mass.
Atoms are electrically neutral, which means that they have an equal number of protons and electrons. If an atom gains or losses one or more electrons, it becomes an ion with a net positive or negative charge, respectively.
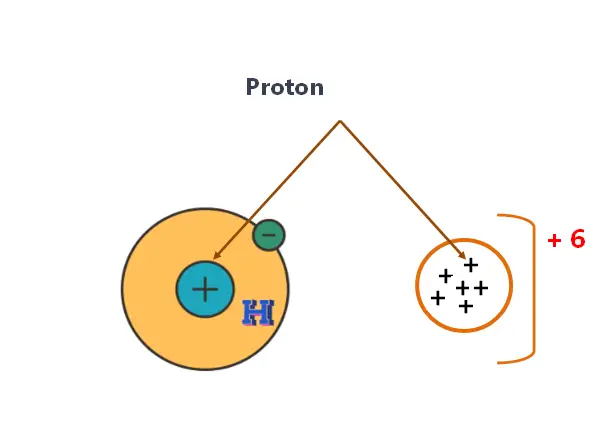
What are protons?
Protons are one of the three primary subatomic particles that make up atoms, along with neutrons and electrons. Protons are positively charged particles. They have a mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit and a charge of +1. Nucleus contains protons.
The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus also determines its chemical properties. The number of protons determines the atom’s overall charge, which affects how it interacts with other atoms in chemical reactions.
Function of proton in atom:
Protons have several important functions in an atom.
Proton determines the atomic number. The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus determines the element it is. For example, an atom with 6 protons is always carbon, while an atom with 8 protons is always oxygen.
Protons contribute to the atomic mass. Protons have a mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu), and the total number of protons in an atom’s nucleus determines a significant portion of the atom’s mass.
Proton helps to stabilize the nucleus. Thepositively charged protons in the nucleus repel each other due to the electromagnetic force. However, the strong nuclear force is able to overcome this repulsion and hold the nucleus together, stabilizing the atom.
Proton determines the charge of the nucleus. Since protons have a positive charge, the total number of protons in an atom’s nucleus determines the net charge of the nucleus. If an atom has the same number of protons and electrons, it is electrically neutral. If there are more protons than electrons, the atom has a positive charge and is called a cation.
Structure of Atom
What are electrons?
An electron is a subatomic particle that has a negative charge and is located outside the nucleus of an atom. The electrons are arranged around the nucleus in energy levels or shells. Electrons have a mass of approximately 1/1836 atomic mass units, and they are negatively charged, with a charge of -1.
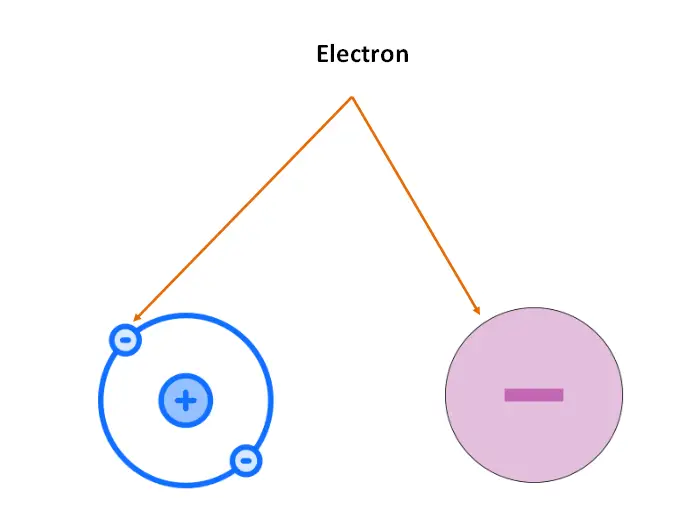
Function of electron in atom:
Electrons have several important functions in an atom. It plays a crucial role in determining the chemical properties and behavior of an atom, as well as its size, ionization potential, and electrical conductivity.
Structure of Atom
Electron determines the chemical behavior of the atom. Electrons are negatively charged and orbit around the nucleus, interacting with other atoms through chemical bonds. The arrangement of electrons around an atom determines the chemical properties of that element and how it reacts with other atoms.
Electron contributes to the atomic size. The electrons surrounding an atom determine the size of the atom. The more electrons an atom has, the larger it will be.
Electron determines the ionization potential. The ionization potential is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. The number and arrangement of electrons in an atom determine its ionization potential, which in turn determines how easily it can lose or gain electrons and form ions.
Electron determines the electrical conductivity. The flow of electric current in a material is largely determined by the movement of electrons. Materials with electrons that are free to move, such as metals, are good conductors of electricity, while materials with electrons that are tightly bound, such as non-metals, are poor conductors of electricity.
What are neutrons?
A neutron is a subatomic particle that is found in the nucleus of an atom along with protons. It has a mass slightly greater than that of a proton.
While protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged, neutrons have no charge and are therefore electrically neutral.
The presence or absence of neutrons in an atom’s nucleus can affect its stability and reactivity, and can also impact the properties and behavior of the element as a whole.
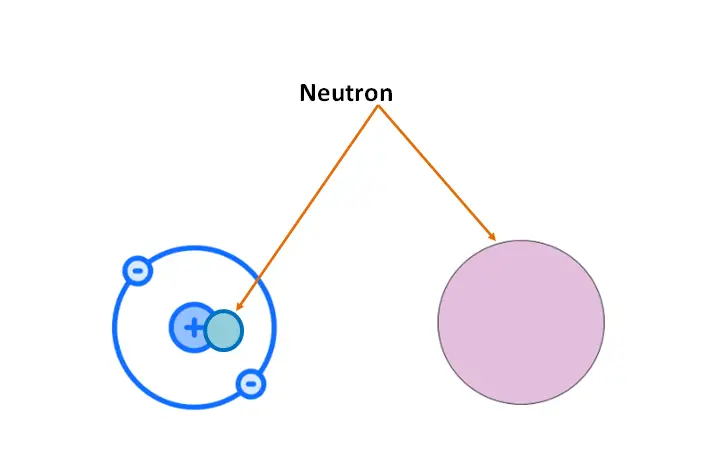
Function of neutron in atom:
Neutron plays a crucial role in determining the properties and behavior of atoms and is essential for our understanding of the structure of matter. It has several important functions in an atom.
1. Neutrons contribute to the atomic mass. The mass of an atom is primarily determined by the sum of its protons and neutrons. Since neutrons have a mass slightly greater than that of protons, they contribute to the overall mass of the atom.
2. Neutron stabilizes the state of nucleus. The presence of neutrons in the nucleus can help stabilize it against repulsion from the positively charged protons. This is because the strong nuclear force, which binds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus, is able to overcome the electromagnetic force that would otherwise cause the protons to repel each other.
3. Neutrons determine isotopes. The number of neutrons in an atom’s nucleus can vary, resulting in different isotopes of the same element. For example, carbon has three naturally occurring isotopes: carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14. Carbon-12 has six neutrons, carbon-13 has seven neutrons, and carbon-14 has eight neutrons. These isotopes have the same number of protons (six) and electron. The different number of neutrons in isotopes affects their stability and radioactivity.
4. Neutrons are involved in nuclear reactions. Neutrons can be added to or removed from a nucleus in nuclear reactions, leading to the formation of new isotopes or the release of energy. This is the basis of nuclear power and nuclear weapons.
Structure of Atom
Related :
